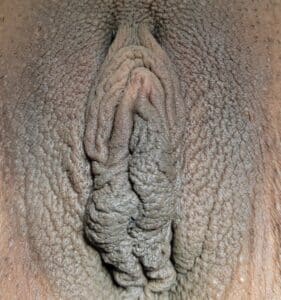
Before
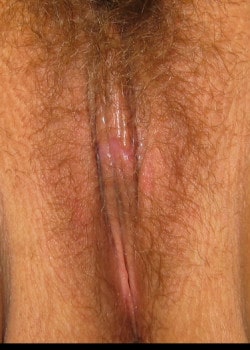
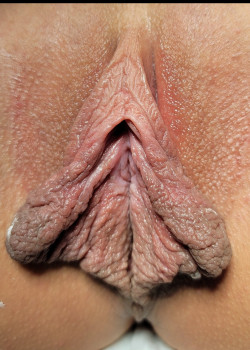
After
Description: Labia Minora Reduction Before and After
Case Details
This patient came to see Dr. Medalie at his Beachwood office asking about labiaplasty which is also known as labia minora reduction. The labia minora are the inner labial lips and can be irritating if they protrude beyond the labia majora (the outer labial lips). The patient had extra tissue which was making it uncomfortable for her to perform normal daily activities. The procedure was done in Dr. Medalie’s office under local anesthesia with mild oral sedation and she is shown only 3 weeks after surgery. This demonstrates how well and quickly the labia heal. Below is information from the American Society of Plastic Surgery that I have added some notes to as well.
What is a labiaplasty?
The term labiaplasty refers to a procedure that reduces the length of the labia minora. It is the most commonly performed vaginal rejuvenation procedure and it can relieve symptoms women experience from twisting and tugging of the labia.
Reasons patients want a labiaplasty
Women opt for surgery for a variety of reasons, including pain from twisting and tugging of the labia when riding a bike or during intercourse, itching, irritation and self-consciousness.
What does a labiaplasty do?
The goal of the procedure is to reduce the labia minora so that they don’t hang below the hair-bearing labia majora. A labiaplasty may be performed to reduce asymmetry when one is longer than the other, or, more commonly, to reduce the length of both labia so that the labia no longer twist, tug or fall out of a bathing suit.
Anesthesia for a labiapasty
Labiaplasty is a procedure that can be done under either local anesthesia with oral sedation or under general anesthesia.
Labiaplasty procedure
The most common type of labiaplasty is the trim procedure, in which the extra tissue is removed and sewn up directly. I personally believe that this is an inferior procedure compared to the wedge resection and almost always perform some type of wedge resection. Next in popularity is the wedge procedure, which maintains a natural border after a pie-shaped piece of tissue has been removed. Extra folds of the clitoral hood can also be reduced at the same time. Closure is usually done with absorbable sutures.
What are the risks of a labiaplasty?
The risks associated with labiaplasty include those of most surgical procedures, including bleeding, hematoma and infection. The most common complication is over-resection (this can occur with trim procedures more than wedge procedures). While some women desire an aggressive reduction, this can result in chronic dryness, scarring at or near the vaginal opening and pain with intercourse. Healing problems are more likely to occur with a wedge procedure, particularly if the patient is exposed to substances that cause blood vessels to shrink (such as smoking).
Recovering from a labiaplasty
Most patients take a week off from work, during which they can reduce swelling and pain by icing with a cold pack sandwiched between the patient’s underpants and an elastic garment, like Spanx. This can be done “twenty minutes on, twenty minutes off.” The patient can also lie with her bottom elevated to reduce swelling.
Patients can resume wearing tampons or having intercourse after four to six weeks.
While the most distorting swelling is gone by 6 weeks, residual swelling may take several months to disappear.
What are the results of a labiaplasty?
Labiaplasty typically results in shorter labia that no longer hang down below the level of the hair-bearing labia majora. Most patients who experienced symptoms from twisting and tugging of their labia generally find relief after surgery. According to multiple studies, labiaplasty surgery is associated with a high satisfaction rate of over 90 percent.